官网
创建元素
Snap(...)
Snap(width,height)
Snap(SVGElement)
Snap(array of elements)
Snap(CSS query selector)
Paper.el(name, attr)
Creates an element on paper with a given name and no attributes
Paper.rect(x, y, width, height, [rx], [ry])
Draws a rectangle
Paper.circle(x, y, r)
Draws a circle
Paper.image(src, x, y, width, height)
Places an image on the surface
Paper.ellipse(x, y, rx, ry)
Draws an ellipse
Paper.text(x, y, text)
Draws a text string
Paper.path([pathString])
Creates a <path> element using the given string as the path’s definition
Paper.line(x1, y1, x2, y2)
Draws a line
Paper.polyline(array|varargs)
Draws a polyline.标签用来创建仅包含直线的形状
var p1 = paper.polyline([10, 10, 100, 100]);
var p2 = paper.polyline(10, 10, 100, 100);
Paper.polygon()
Draws a polygon. See Paper.polyline
Paper.g([varargs])
Paper.group()
Creates a group element
var c1 = paper.circle(),
c2 = paper.rect(),
g = paper.g(c2, c1); // note that the order of elements is different
or
var c1 = paper.circle(),
c2 = paper.rect(),
g = paper.g();
g.add(c2, c1);
Paper.mask() 蒙版
Equivalent in behaviour to Paper.g, except it’s a mask.
Element.marker(x, y, width, height, refX, refY)
Creates a <marker> element from the current element To create a marker you have to specify the bounding rect and reference point.marker-start, marker-end, marker-mid, and marker attributes.
Paper.ptrn(x, y, width, height, vbx, vby, vbw, vbh)
Equivalent in behaviour to Paper.g, except it’s a pattern.
Paper.use(id)
Creates a <use> element.
Paper.symbol(vbx, vby, vbw, vbh)
Creates a <symbol> element.
Element.clone()
Creates a clone of the element and inserts it after the element
Element.toDefs()
Moves element to the shared <defs> area
Element.toPattern(x, y, width, height)
Creates a <pattern> element from the current element To create a pattern you have to specify the pattern rect
Gradient
Paper.gradient(gradient)
Creates a gradient element
The gradient descriptor is an expression formatted as follows: <type>(<coords>)<colors>.
- The
<type>can be eitherlinearorradial. - The uppercase
LorRletters indicateabsolute coordinatesoffset from the SVG surface. Lowercaselorrletters indicate coordinates calculatedrelative tothe element to which the gradient is applied. Coordinates specify alinear gradientvector asx1,y1,x2,y2, or aradial gradientascx,cy,rand optional fx, fy specifying a focal point away from the center of the circle. - Specify
<colors>as a list of dash-separated CSS color values. Each color may be followed by a custom offset value, separated with a colon character.
//Linear gradient, relative from top-left corner to bottom-right corner, from black through red to white
var g = paper.gradient("l(0, 0, 1, 1)#000-#f00-#fff");
//Linear gradient, absolute from (0, 0) to (100, 100), from black through red at 25% to white:
var g = paper.gradient("L(0, 0, 100, 100)#000-#f00:25-#fff");
//Radial gradient, relative from the center of the element with radius half the width, from black to white
var g = paper.gradient("r(0.5, 0.5, 0.5)#000-#fff");
//To apply the gradient:
paper.circle(50, 50, 40).attr({
fill: g
});
Element.addStop(color, offset)
Only for gradients! Adds another stop to the gradient.
Element.setStops(str)
Only for gradients! Updates stops of the gradient based on passed gradient descriptor. See paper.gradient
Element.stops()
Only for gradients! Returns array of gradient stops elements.
Filter
Paper.filter(filstr)
Creates a <filter> element
Snap.filter.blur(x, [y])
Returns an SVG markup string for the blur filter
Snap.filter.shadow(…)
Returns an SVG markup string for the shadow filter
Parameters:
dx,dy,blur,color,opacity / dx,dy,color,opacity / dx,dy,pixels,opacity
Snap.filter.grayscale(amount)
Returns an SVG markup string for the grayscale filter
Snap.filter.sepia(amount)
Returns an SVG markup string for the sepia filter
Snap.filter.saturate(amount)
Returns an SVG markup string for the saturate filter
Snap.filter.hueRotate(angle)
Returns an SVG markup string for the hue-rotate filter
Snap.filter.invert(amount)
Returns an SVG markup string for the invert filter
Snap.filter.brightness(amount)
Returns an SVG markup string for the brightness filter
Snap.filter.contrast(amount)
Returns an SVG markup string for the contrast filter
Path
Paper.path([pathString])
Creates a <path> element using the given string as the path’s definition
Snap.path.getTotalLength(path)
Returns the length of the given path in pixels
Snap.path.getPointAtLength(path, length)
Returns the coordinates of the point located at the given length along the given path
Snap.path.getSubpath(path, from, to)
Returns the subpath of a given path between given start and end lengths
Snap.path.findDotsAtSegment(p1x, p1y, c1x, c1y, c2x, c2y, p2x, p2y, t)
Utility method Finds dot coordinates on the given cubic beziér curve at the given t
Snap.path.bezierBBox(…)
Utility method Returns the bounding box of a given cubic beziér curve
Snap.path.isPointInsideBBox(bbox, x, y)
Utility method Returns true if given point is inside bounding box
Snap.path.isBBoxIntersect(bbox1, bbox2)
Utility method Returns true if two bounding boxes intersect
Snap.path.intersection(path1, path2)
Utility method Finds intersections of two paths
Snap.path.isPointInside(path, x, y)
Utility method Returns true if given point is inside a given closed path.
Snap.path.getBBox(path)
Utility method Returns the bounding box of a given path
Snap.path.toRelative(path)
Utility method Converts path coordinates into relative value
Snap.path.toAbsolute(path)
Utility method Converts path coordinates into absolute values
Snap.path.toCubic(pathString)
Utility method Converts path to a new path where all segments are cubic beziér curves
Snap.path.map(path, matrix)
Transform the path string with the given matrix
Snap.closestPoint(path, x, y)
Returns closest point to a given one on a given path.
查找元素
Snap.select(query)
Wraps a DOM element specified by CSS selector as Element
Snap.selectAll(query)
Wraps DOM elements specified by CSS selector as set or array of Element
Element.select(query)
Gathers the nested Element matching the given set of CSS selectors
Element.selectAll(query)
Gathers nested Element objects matching the given set of CSS selectors
Fragment.select()
See Element.select
Fragment.selectAll()
See Element.selectAll
Element.node()
Gives you a reference to the DOM object, so you can assign event handlers or just mess around.
Element.children()
Returns array of all the children of the element.
Element.parent()
Returns the element’s parent
元素信息
Element.type()
SVG tag name of the given element.
Snap.getElementByPoint(x, y)
Returns you topmost element under given point.
Snap.getElementByPoint(mouseX, mouseY).attr({stroke: "#f00"});
Element.getBBox()
Returns the bounding box descriptor for the given element
Element.asPX(attr, [value])
Returns given attribute of the element as a px value (not %, em, etc.)
Element.data(key, [value])
Adds or retrieves given value associated with given key. (Don’t confuse with data- attributes)
Element.removeData([key])
Removes value associated with an element by given key. If key is not provided, removes all the data of the element.
操作元素
Element.outerSVG()
Returns SVG code for the element, equivalent to HTML’s outerHTML.
Element.innerSVG()
Paper.toString()
Returns SVG code for the Paper
Snap.deurl(value)
Unwraps path from “url(<path>)”.
Paper.toDataURL()
Returns SVG code for the Paper as Data URI string.
Element.toJSON()
Returns object representation of the given element and all its children.
Snap.ajax(…)
Simple implementation of Ajax
Snap.load(url, callback, [scope])
Loads external SVG file as a Fragment (see Snap.ajax for more advanced AJAX)
Paper.clear()
Removes all child nodes of the paper, except <defs>.
Element.attr(…)
Gets or sets given attributes of the element.
Element.transform(tstr)
Gets or sets transformation of the element
Element.parent()
Returns the element’s parent
Element.append(el)
Appends the given element to current one
Element.appendTo(el)
Appends the current element to the given one
Element.prepend(el)
Prepends the given element to the current one
Element.prependTo(el)
Prepends the current element to the given one
Element.before(el)
Inserts given element before the current one
Element.after(el)
Inserts given element after the current one
Element.insertBefore(el)
Inserts the element after the given one
Element.insertAfter(el)
Inserts the element after the given one
Element.remove()
Removes element from the DOM
事件
Element.click(handler)
Adds a click event handler to the element
Element.unclick(handler)
Removes a click event handler from the element
Element.dblclick(handler)
Adds a double click event handler to the element
Element.mousedown(handler)
Adds a mousedown event handler to the element
Element.mousemove(handler)
Adds a mousemove event handler to the element
Element.mouseout(handler)
Adds a mouseout event handler to the element
Element.mouseover(handler)
Adds a mouseover event handler to the element
Element.mouseup(handler)
Adds a mouseup event handler to the element
Element.touchstart(handler)
Adds a touchstart event handler to the element
Element.touchmove(handler)
Adds a touchmove event handler to the element
Element.touchend(handler)
Adds a touchend event handler to the element
Element.touchcancel(handler)
Adds a touchcancel event handler to the element
Element.hover(f_in, f_out, [icontext], [ocontext])
Adds hover event handlers to the element
Element.drag(onmove, onstart, onend, [mcontext], [scontext], [econtext])
Adds event handlers for an element’s drag gesture
动画
Snap.animate(from, to, setter, duration, [easing], [callback])
Runs generic animation of one number into another with a caring function
var rect = Snap().rect(0, 0, 10, 10);
Snap.animate(0, 10, function (val) {
rect.attr({
x: val
});
}, 1000);
// in given context is equivalent to
rect.animate({x: 10}, 1000);
Element.animate(attrs, duration, [easing], [callback])
Animates the given attributes of the element
Element.inAnim()
Returns a set of animations that may be able to manipulate the current element
缓动函数
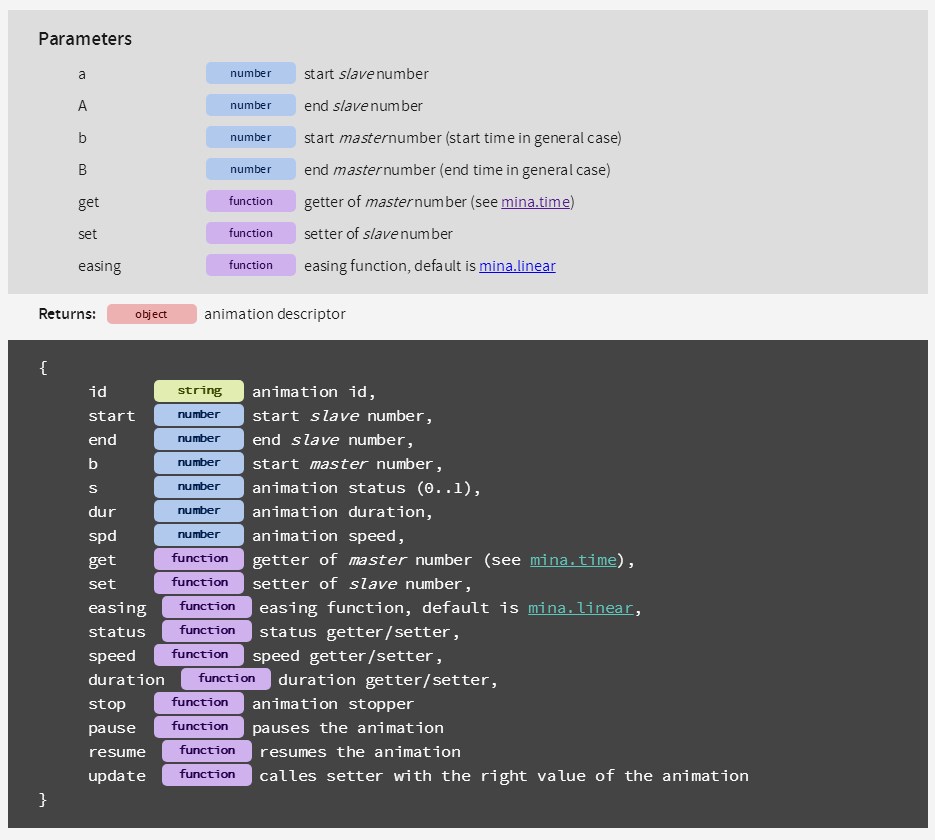
mina(a, A, b, B, get, set, [easing])
Generic animation of numbers
<svg id="svg" width="200" height="100"></svg>
<input id="button" type="button" class="zxx_api_button" value="点击运行">
var c = Snap("#svg").paper.circle(50,50,40).attr({ fill: "red" });
document.getElementById("button").onclick = function() {
var now = mina.time();
var ani = mina(50, 150, now, now + 1000, mina.time, function(val) {
c.attr({
cx: val
});
}, mina.easeout);
console.dir(ani);
};
mina.time()
Returns the current time. Equivalent to:
mina.getById(id)
Returns an animation by its id
mina.linear(n)
Default linear easing
mina.easeout(n)
Easeout easing
mina.easeout(n)
Easeout easing
mina.easein(n)` Easein easing
mina.easeinout(n)
Easeinout easing
mina.backin(n)
Backin easing
mina.backout(n)
Backout easing
mina.elastic(n)
Elastic easing
mina.bounce(n)
Bounce easing
矩阵
工具
格式解析
Snap.format(token, json)
Replaces construction of type {<name>} to the corresponding argument
// this draws a rectangular shape equivalent to "M10,20h40v50h-40z"
paper.path(Snap.format("M{x},{y}h{dim.width}v{dim.height}h{dim['negative width']}z", {
x: 10,
y: 20,
dim: {
width: 40,
height: 50,
"negative width": -40
}
}));
Snap.url(value)
Wraps path into "url('<path>')".
Snap.is(o, type)`
Handy replacement for the typeof operator
距离
Snap.snapTo(values, value, [tolerance])`
Snaps given value to given grid 在指定的数组栅格中找到输入数值合适的数
tolerance:maximum distance to the target value that would trigger the snap. Default is 10.
Snap.snapTo([10,20,30,40], 11);
//输出:20
Snap.snapTo([10,20,30,40], 11,5);
//输出:10
Snap.closestPoint(path, x, y)
Returns closest point to a given one on a given path.
Snap.len(x1, y1, x2, y2)`
Returns distance between two points
Snap.len2(x1, y1, x2, y2)`
Returns squared distance between two points
Snap.parsePathString(pathString)
Utility method Parses given path string into an array of arrays of path segments
Snap.parsePathString('M42 56L75 56L75 636L108 636')
/*输出:
(4) [Array(3), Array(3), Array(3), Array(3), toString: ƒ]
0:(3) ["M", 42, 56]
1:(3) ["L", 75, 56]
2:(3) ["L", 75, 636]
3:(3) ["L", 108, 636]
*/
Snap.parseTransformString(TString)
Utility method Parses given transform string into an array of transformations
Snap.parseTransformString("t20,20s2,1,0,0");
/*输出:
(2) [Array(3), Array(5), toString: ƒ]
0:Array(3)
0:"t"
1:20
2:20
length:3
__proto__:Array(0)
1:Array(5)
0:"s"
1:2
2:1
3:0
4:0
length:5
__proto__:Array(0)
*/
弧度、角度
Snap.rad(deg)
Transform angle to radians 角度转换为弧度
Snap.deg(rad)
Transform angle to degrees 弧度转换为角度
Snap.sin(angle)
Equivalent to Math.sin() only works with degrees, not radians.
Snap.tan(angle)
Equivalent to Math.tan() only works with degrees, not radians.
Snap.cos(angle)
Equivalent to Math.cos() only works with degrees, not radians.
Snap.asin(num)
Equivalent to Math.asin() only works with degrees, not radians.
Snap.acos(num)
Equivalent to Math.acos() only works with degrees, not radians.
Snap.atan(num)
Equivalent to Math.atan() only works with degrees, not radians.
Snap.atan2(num)
Equivalent to Math.atan2() only works with degrees, not radians.
Snap.angle(x1, y1, x2, y2, [x3], [y3])
Returns an angle between two or three points
颜色
Snap.mui
Contain Material UI colours.
Snap().rect(0, 0, 10, 10).attr({fill: Snap.mui.deeppurple, stroke: Snap.mui.amber[600]});
Snap.flat
Contain Flat UI colours.
Snap().rect(0, 0, 10, 10).attr({fill: Snap.flat.carrot, stroke: Snap.flat.wetasphalt});
Snap.importMUIColors()
Imports Material UI colours into global object.
Snap.importMUIColors();
Snap().rect(0, 0, 10, 10).attr({fill: deeppurple, stroke: amber[600]});
Snap.color(clr)
Parses the color string and returns an object featuring the color’s component values
Snap.hsb(h, s, b)
Converts HSB values to a hex representation of the color
Snap.hsl(h, s, l)
Converts HSL values to a hex representation of the color
Snap.rgb(r, g, b)
Converts RGB values to a hex representation of the color
Snap.getRGB(color)
Parses color string as RGB object
Snap.hsb2rgb(h, s, v)
Converts HSB values to an RGB object
Snap.hsl2rgb(h, s, l)
Converts HSL values to an RGB object
Snap.rgb2hsb(r, g, b)
Converts RGB values to an HSB object
Snap.rgb2hsl(r, g, b)
Converts RGB values to an HSL object