files
files 定义了哪些文件应该被包括在 npm install 后的 node_modules 中。
有些文件是自动暴露出来的,不管你是不是配置了 files,比如:
- package.json
- README / CHANGELOG / LICENSE
vite 中是这样配置的:
{
"files": ["bin", "dist", "client.d.ts"]
}
bin
bin 列出了可执行文件,表示你这个包要对外提供哪些脚本。
在这个包被 install 安装时,如果是全局安装 -g,bin 列出的可执行文件会被添加到 PATH 变量(全局可执行);如果是局部安装,则会进入到 node_modules/.bin/ 目录下。
bin 在一些 CLI 工具中用得很频繁,比如 Vue CLI。
在开发 npm 包时,要求发布的可执行脚本要以#!/usr/bin/env node开头,用于指明该脚本文件要使用 node 来执行。
typings
{
"typings": "dist/src"
}
ts .d 文件的路径
engines
{
"engines": {
"node": ">=16",
"pnpm": ">=6"
}
}
repository
{
"repository": {
"type": "git",
"url": "https://xxxx/xxxx/xxxx.git"
}
}
publishConfig
{
"publishConfig": {
"registry": "https://xxxx/repository/xxx/"
}
}
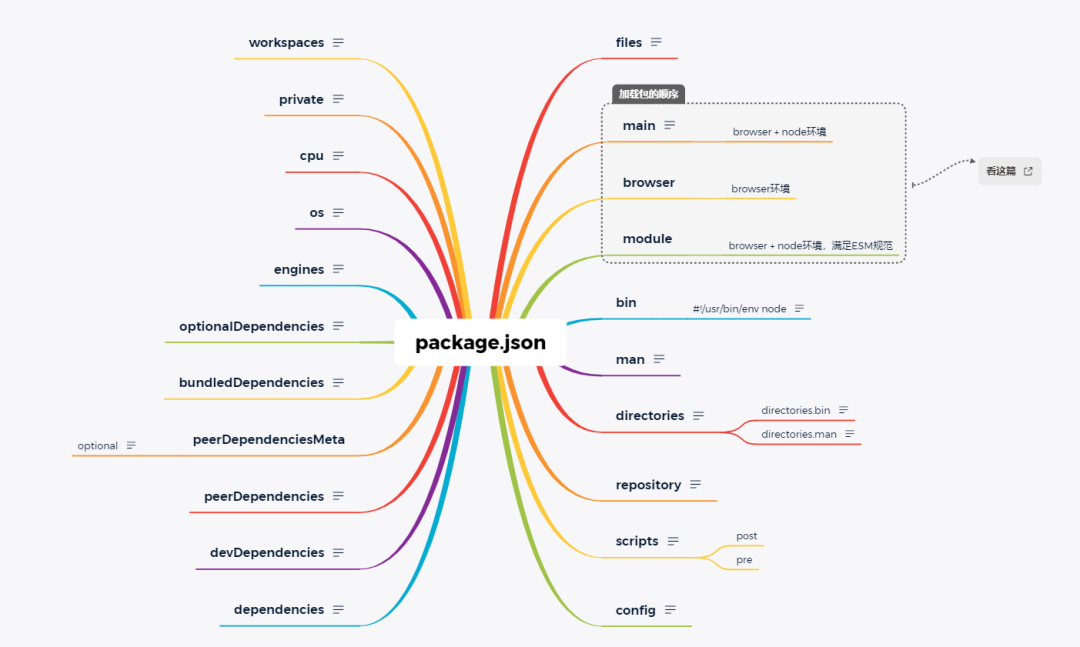
main, browser, module
文件优先级
我们使用的模块规范有 ESM 和 commonJS 两种,为了能在 node 环境下原生执行 ESM 规范的脚本文件,.mjs 文件就应运而生。
Node 原始的模块方式 CommonJS 简称为 CJS,而 ES Module 称为 ESM。
当存在 index.mjs 和 index.js 这种同名不同后缀的文件时,import './index' 或者 require('./index') 是会优先加载 index.mjs 文件
mjs > js
字段定义
main: 定义了 npm 包的入口文件,browser 环境和 node 环境均可使用module: 定义 npm 包的 ESM 规范的入口文件,browser 环境和 node 环境均可使用browser: 定义 npm 包在 browser 环境下的入口文件
npm 包
- 如果 npm 包导出的是
ESM规范的包,使用module - 如果 npm 包只在
web端使用,并且严禁在 server 端使用,使用browser。 - 如果 npm 包只在
server端使用,使用main - 如果 npm 包在
web端和server端都允许使用,使用browser和main
scripts
每次在运行 scripts 中的一个属性时候(npm run),实际系统都会自动新建一个 shell(一般是 Bash),在这个 shell 里面执行指定的脚本命令。因此凡是能在 shell 中允许的脚本,都可以写在 npm scripts 中。
npm run 新建的 shell,会在当前目录的node_modules/.bin子目录加入到 PATH 变量,执行结束后,再将 PATH 变量恢复原样。也就是说,当前项目目录node_modules/.bin子目录中所有的脚本,都可以直接用脚本名称调用,不需要增加路径.(简单总结:通过 npm 启动的脚本,会默认把node_modules/.bin加到 PATH 环境变量中。)
脚本默认值
"start": "node server.js"
"install": "node-gyp rebuild"
钩子(生命周期)
npm 脚本有两个钩子,pre 和 post,当我们执行start脚本时候,start 的钩子就是 prestart 和 poststart。
当我们执行 npm run start 的时候,npm 会自动按照下面的顺序执行:
npm run prestart && npm run start && npm run poststart
pre:在一个 script 执行前执行,比如 prebuild,可以在打包前做一些准备工作。post:在一个 script 执行后执行,比如 postbuild,可以在打包后做一些收尾工作。
config
通过config配置的参数xxx,可以在脚本中通过npm_package_config_xxx 的形式引用,比如port。
{
"config": {
"port": "8080"
}
}
依赖相关
dependencies
dependencies可以理解为生产依赖,通过npm install --save安装的依赖包都会进入到 dependencies 中。
# 安装当前npm仓库中这个包的最新版本
npm install/i packageName -S/--save
# 如果要指定版本的,可以把版本号写在包名后面
npm i packageName@3.0.1 -S
{
"dependencies": {
"foo": "1.0.0 - 2.9999.9999", // 指定版本范围
"bar": ">=1.0.2 <2.1.2",
"baz": ">1.0.2 <=2.3.4",
"boo": "2.0.1", // 指定版本
"qux": "<1.0.0 || >=2.3.1 <2.4.5 || >=2.5.2 <3.0.0",
"asd": "http://asdf.com/asdf.tar.gz", // 指定包地址
"til": "~1.2", // 最近可用版本
"elf": "~1.2.3",
"elf": "^1.2.3", // 兼容版本
"two": "2.x", // 2.1、2.2、...、2.9皆可用
"thr": "*", // 任意版本
"thr2": "", // 任意版本
"lat": "latest", // 当前最新
"dyl": "file:../dyl", // 本地地址
"xyz": "git+ssh://git@github.com:npm/npm.git#v1.0.27", // git 地址
"fir": "git+ssh://git@github.com:npm/npm#semver:^5.0",
"wdy": "git+https://isaacs@github.com/npm/npm.git",
"xxy": "git://github.com/npm/npm.git#v1.0.27"
}
}
devDependencies
devDependencies可以理解为开发环境依赖,通常是一些工具类的包,比如 webpack, babel 等。通过npm install --save-dev安装的依赖包都会进入到devDependencies中。
npm install/i packageName -D/--save-dev
peerDependencies
同等依赖,或者叫同伴依赖,用于指定当前包(也就是你写的包)兼容的宿主版本。
例如,我们编写一个 gulp 的插件,而 gulp 却有多个主版本,我们只想兼容最新的版本,此时就可以用同等依赖(peerDependencies)来指定:
{
"name": "gulp-my-plugin",
"version": "0.0.1",
"peerDependencies": {
"gulp": "3.x"
}
}
当别人使用我们的插件时,peerDependencies就会告诉明确告诉使用方,你需要安装该插件哪个宿主版本。
通常情况下,我们会在一个项目里使用一个宿主(比如 gulp)的很多插件,如果相互之间存在宿主不兼容,在执行npm install时,cli会抛出错误信息来告诉我们,比如:
npm ERR! peerinvalid The package gulp does not satisfy its siblings' peerDependencies requirements!'
npm ERR! peerinvalid Peer gulp-cli-config@0.1.3 wants gulp@~3.1.9
npm ERR! peerinvalid Peer gulp-cli-users@0.1.4 wants gulp@~2.3.0
运行命令npm install gulp-my-plugin --save-dev来安装我们插件
bundledDependencies
bundledDependencies跟上面的依赖都不太一样,配置上不是键值对的形式,而是一个数组。包必须先在devDependencies或dependencies声明过,否则打包会报错。
{
"bundledDependencies": ["vue", "vue-router"]
}
在运行npm pack时,会将对应依赖打包到tgz文件中。用得不多,不知道具体的细节,主要还是直接用npm install安装 tgz 包的场景比较少,有个概念就行。
optionalDependencies
可选依赖,如果有一些依赖包即使安装失败,项目仍然能够运行或者希望 npm 继续运行,就可以使用optionalDependencies。另外optionalDependencies会覆盖dependencies中的同名依赖包,所以不要在两个地方都写。
optionalDependencies用于配置可选的依赖,即使配了这个,代码里也要做好判断(保护),否则运行报错就不好玩了。
try {
var foo = require("foo");
var fooVersion = require("foo/package.json").version;
} catch (er) {
foo = null;
}
funding
指定一个包含 URL 的对象,该 URL 提供有关帮助资助包开发的方法的最新信息,或字符串 URL,或以下数组:
{
"funding": {
"type": "individual",
"url": "http://example.com/donate"
},
"funding": {
"type": "patreon",
"url": "https://www.patreon.com/my-account"
},
"funding": "http://example.com/donate",
"funding": [
{
"type": "individual",
"url": "http://example.com/donate"
},
"http://example.com/donateAlso",
{
"type": "patreon",
"url": "https://www.patreon.com/my-account"
}
]
}
npm fund
npm fund <projectname>