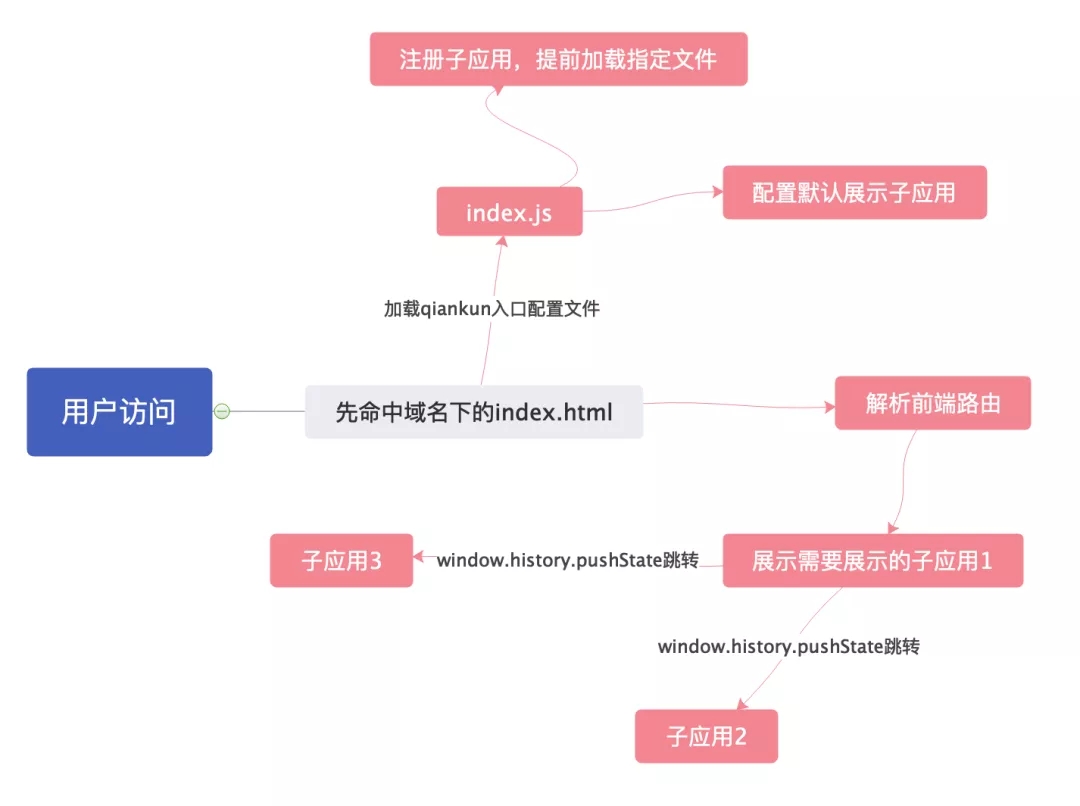
现在微前端模式分很多种,但是大都是一个基座+多个子应用模式,根据子应用注册的规则,去展示子应用。目前的微前端框架基座加载模式的原理,基于single-spa封装了一层
基座搭建,这里使用parcel:
yarn init
yarn add --dev parcel@next
cnpm install -g nodemon
cnpm install express
目录结构
-.parcel-cache
-dist
-example
-server
-subApp1.js
-subApp2.js
-subApp1
-index.html
-subApp2
-index.html
-src
-index.js
-route.js
-index.html
-index.j
-package.json
-yarn.lock
基座路由
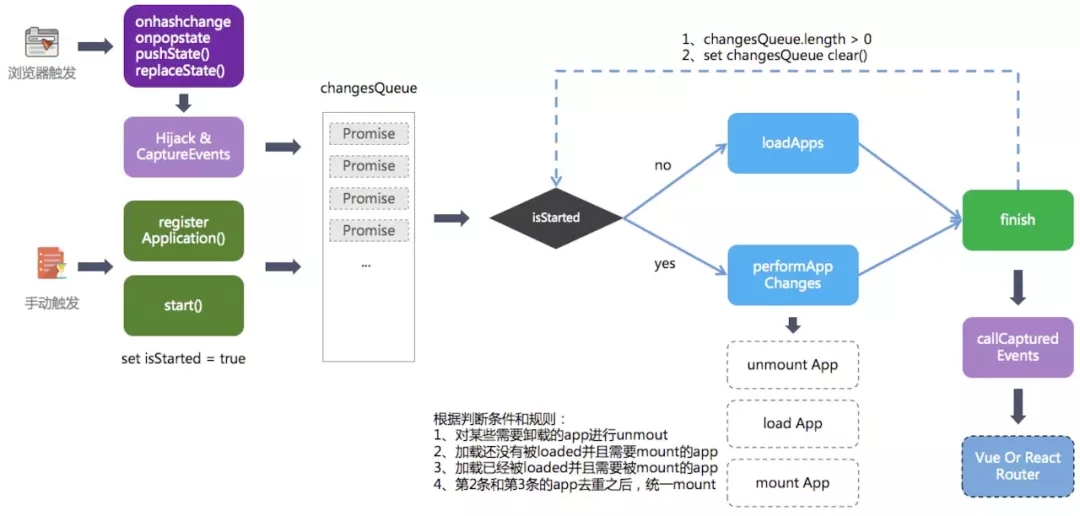
src\index.js
const HIJACK_EVENTS_NAME = /^(hashchange|popstate)$/i;
// 创建两个队列,使用数组实现
const EVENTS_POOL = {
hashchange: [],
popstate: []
};
const originAddEventListener = window.addEventListener;
const originRemoveEventListener = window.removeEventListener;
window.addEventListener = function (eventName, handler) {
// 拦截事件绑定方法
// 监听检测到是 hashchange popstate 类型事件, 而且它们对应的回调函数不存在队列中时候,放入队列中
if (eventName && HIJACK_EVENTS_NAME.test(eventName) &&
typeof handler === 'function') {
EVENTS_POOL[eventName].indexOf(handler) === -1 &&
EVENTS_POOL[eventName].push(handler);
}
return originAddEventListener.apply(this, arguments);
}
window.removeEventListener = function (eventName, handler) {
if (eventName && HIJACK_EVENTS_NAME.test(eventName)) {
let eventsList = EVENTS_POOL[eventName];
//移除事件池中对应的 hashchange popstate 事件
eventsList.indexOf(handler) > -1 &&
(EVENTS_POOL[eventName] = eventsList.filter((fn) => fn !== handler));
}
return originRemoveEventListener.apply(this, arguments);
}
window.addEventListener('popstate', function () {
console.log("popstate");
history.replaceState({}, null, location.hash.replace(/#/, ""));
loadApp();
});
function mockPopStateEvent(state) {
return new PopStateEvent('popstate', { state });
}
// 拦截history的方法,因为pushState和replaceState方法并不会触发onpopstate事件
// 所以即便在onpopstate时执行了reroute方法,也要在这里执行下reroute方法。
const originalPushState = window.history.pushState;
const originalReplaceState = window.history.replaceState;
window.history.pushState = function (state, title, url) {
let result = originalPushState.apply(this, arguments);
// history.pushState()或history.replaceState()不会触发popstate事件
// 手动执行触发 popstate 事件
reRoute(mockPopStateEvent(state));
return result;
}
window.history.replaceState = function (state, title, url) {
let result = originalReplaceState.apply(this, arguments);
reRoute(mockPopStateEvent(state));
return result;
}
// 执行完load、mount、unmout操作后,执行此函数,就可以保证微前端的逻辑总是第一个执行。
// 然后App中的Vue或React相关Router就可以收到Location的事件了。
export function callCapturedEvents(eventArgs) {
if (!eventArgs) {
return;
}
if (!Array.isArray(eventArgs)) {
eventArgs = [eventArgs];
}
let name = eventArgs[0].type;
if (!HIJACK_EVENTS_NAME.test(name)) {
return;
}
EVENTS_POOL[name].forEach((handler) => {
handler.apply(window, eventArgs);
});
}
// 每次监听到路由变化,调用reRoute函数
// 这样每次路由切换,最先知道变化的是基座
// 等基座同步执行完(阻塞)后,就可以由子应用的vue-Rourer或者react-router-dom等库去接管实现单页面逻辑了
function reRoute(popstate) {
//invoke([],arguments);
}
const Apps = [];
export function registryApp(entry, activeRule) {
Apps.push({
entry,
activeRule
});
}
//根据传入的规则去判断是否需要此时挂载
function shouldBeActive(app) {
return app.activeRule(window.location);
}
export async function loadApp() {
const shouldMountApp = Apps.filter(shouldBeActive);
if (!(shouldMountApp && shouldMountApp.length > 0)) {
return;
}
console.log(shouldMountApp[0], 'shouldMountApp');
//可以参考微前端和第三方库的源码,例如import-html-entry这个库
fetch(shouldMountApp[0].entry)
.then(function (response) {
return response.text();
})
.then(function (text) {
const dom = document.createElement('div')
dom.innerHTML = text;
console.log(dom, 'dom');
const content = dom.querySelector('h1');
const subapp = document.querySelector('#subApp');
if (subapp) {
subapp.innerHTML = '';
subapp.appendChild(content);
}
});
}
export function start() {
loadApp();
}
每次路由切换,最先知道变化的是基座,等基座同步执行完(阻塞)后,就可以由子应用的vue-Rourer或者react-router-dom等库去接管实现单页面逻辑了。
加载子应用
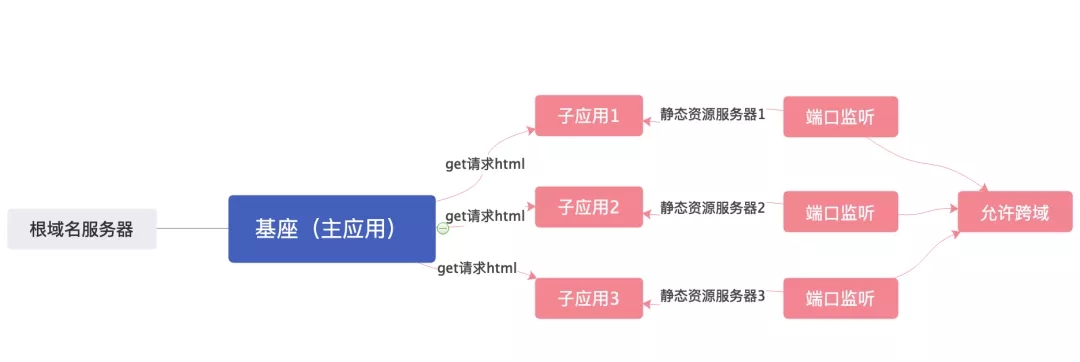
一共四个端口,nginx反向代理命中基座服务器监听的端口(用户必须首先访问到根据域名),然后去不同子应用下的服务器拉取静态资源然后加载。
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>micro-frontend</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<h1>基座</h1>
<div class="subapp">
<div>
<a href="#/subapp1">子应用1</a>
</div>
<div>
<a href="#/subapp2">子应用2</a>
</div>
</div>
<div id="subApp"></div>
</div>
</body>
<script src="index.js" ></script>
</html>
index.js
import {registryApp,start} from './src/index.js'
registryApp('http://localhost:8889', (location) => location.pathname === '/subapp1');
registryApp('http://localhost:8890', (location) => location.pathname === '/subapp2');
start()
example/server/subApp1.js
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const { resolve } = require('path');
//设置跨域访问
app.all('*', function (req, res, next) {
res.header('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*');
res.header('Access-Control-Allow-Headers', 'X-Requested-With');
res.header('Access-Control-Allow-Methods', 'PUT,POST,GET,DELETE,OPTIONS');
res.header('X-Powered-By', ' 3.2.1');
//res.header('Content-Type', 'application/json;charset=utf-8');
next();
});
// 启动 example/subApp1/index.html
app.use(express.static(resolve(__dirname, '../subApp1')));
app.listen(8889, (err) => {
!err && console.log('app1:8889端口成功');
});
example/server/subApp2.js
...
app.use(express.static(resolve(__dirname, '../subApp2')));
app.listen(8889, (err) => {
!err && console.log('app2:8890端口成功');
});
启动服务
yarn parcel index.html
nodemon nodemon example/server/subApp1.js
nodemon nodemon example/server/subApp2.js