SPA vs MPA
| 单页面应用(SinglePage Web Application,SPA) | 多页面应用(MultiPage Application,MPA) | |
|---|---|---|
| 组成 | 一个外壳页面和多个页面片段组成 | 多个完整的页面构成 |
| 资源共用(js,css) | 共用,只需要在外壳部分加载 | 不共用,每个页面都需要加载 |
| 刷新方式 | 页面局部刷新或更改 | 整页刷新 |
| url模式 | a.com/#/pageone | a.com/pageone.html |
| 用户体验 | 页面片段间的切换快,用户体验良好 | 页面切换加载缓慢,流畅度不够,用户体验比较差 |
| 转场动画 | 容易实现 | 无法实现 |
| 数据传递 | 容易 | 依赖url传参、或者cookie、localStorage等 |
| 搜索引擎优化(SEO) | 需要单独方案、实现较为困难、不利于SEO检索 可利用服务器端渲染(SSR)优化 | 实现方法简易 |
| 适用范围 | 高要求的体验度、追求界面流畅的应用 | 追求高度支持搜索引擎的应用 |
| 开发成本 | 较高,常需借助专业的框架 | 较低,但页面重复代码多 |
| 维护成本 | 相对容易 | 相对复杂 |
SPA路由
- 浏览器的url地址发生变化,但是其实并没有发送请求,也没有刷新整个页面
- 根据我们配置的路由信息,每次点击切换路由,会切换到不同的组件显示,类似于选项卡功能的实现,但是同时url地址栏会变化
- 分为
HashRouter和BrowserRouter两种模式
Hash
hash 就是指 url 后的 # 号以及后面的字符。例如www.baidu.com/#segmentfault,那么#segmentfault就是hash值
window.location.hash = '**'设置当前的hash值;const hash = window.location.hash获取当前的hash值hash改变会触发window的hashchange事件
使用类似发布订阅模式的方式:
class Router{
constructor(){
this.routes = {};
this.currentURL = '';
}
route(path,callback){
this.routes[path] = callback || function(){};
}
updateView(){
this.currentURL = location.hash.slice(1)||'/';
this.routes[this.currentURL]&& this.routes[this.currentURL]();
}
init(){
window.addEventLister('load',this.updateView.bind(this),false);
window.addEventLister('hashchage',this.updateView.bidn(this),false);
}
}
routes用来存放不同路由对应的回调函数init用来初始化路由,在load事件发生后刷新页面,并且绑定hashchange事件,当hash值改变时触发对应回调函数
<div id="app">
<ul>
<li>
<a href="#/">home</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#/about">about</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#/topics">topics</a>
</li>
</ul>
<div id="content"></div>
</div>
const router = new Router();
router.init();
router.route('/',function(){
document.getElementById('content').innerHTML = 'Home';
});
router.route('/about',function(){
document.getElementById('content').innerHTML = 'About';
});
router.route('/topics', function () {
document.getElementById('content').innerHTML = 'Topics';
});
History
- History来自Html5的规范
- History模式,url地址栏的改变并不会触发任何事件
- History模式,可以使用
history.pushState,history.replaceState来控制url地址history.pushState()在保留现有历史记录的同时,将 url 加入到历史记录中。history.replaceState()会将历史记录中的当前页面历史替换为 url。
- History模式下,刷新页面会404,需要后端配合匹配一个任意路由,重定向到首页,特别是加上Nginx反向代理服务器的时候
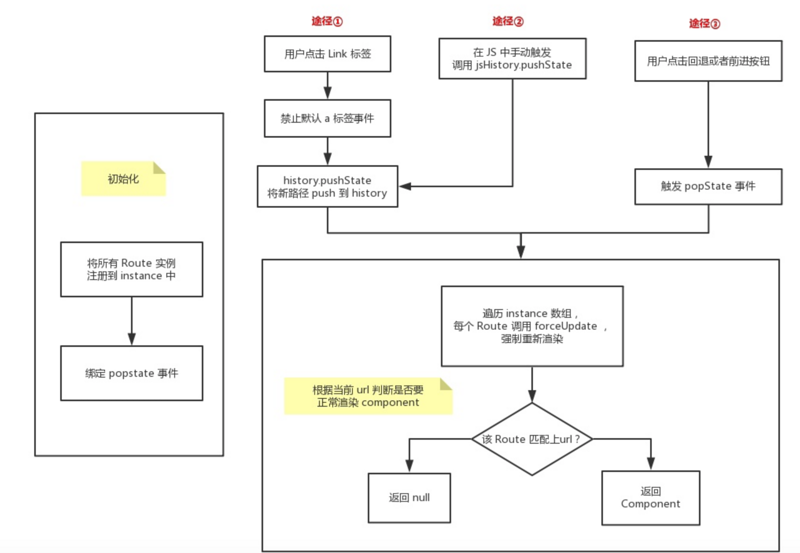
url 的改变(不包括 hash 值得改变)只能由下面三种情况引起:
- 点击浏览器的前进或后退按钮
- 点击
a标签 - 在 JS 代码中触发
history.push(replace)State函数
class Router(){
constructor(){
this.routes = {};
this.currentURL = '';
}
route(path,callback){
this.routes[path] = callback || function(){};
}
updateView(url){
this.currentUrl = url;
this.routes[this.currentUrl] && this.routes[this.currentUrl]();
}
pushState(url){
history.pushState({},null,url);
this.updateView(url);
}
bindLink(){
const allLink = document.querySelectorAll('a[data-href]');
for(let i=0,len =allLink.length;i<len;i++){
const current =allLink[i];
current.addEventLister('click',e=>{
e.preventDefault();
const url = current.getAttribute('data-href');
this.pushState(url);
},false);
}
}
init(){
this.bindLink();
window.addEventListener('popstate',e=>{
this.updateView(window.location.pathname);
});
window.addEventListener('load',()=>{
this.updateView('/',false);
});
}
}
init初始化函数,首先需要获取所有特殊的链接标签,然后监听点击事件,并阻止其默认事件,触发history.pushState以及更新相应的视图。- 绑定
popstate事件,当用户点击前进或者后退的按钮时候,能够及时更新视图,另外当刚进去页面时也要触发一次视图更新。
<div id="app">
<ul>
<li><a data-href="/" href="#">home</a></li>
<li><a data-href="/about" href="#">about</a></li>
<li><a data-href="/topics" href="#">topics</a></li>
</ul>
<div id="content"></div>
</div>