网站链接
Installation
$ npm install stylus -g
Watch and compile a stylus file from command line with
stylus -w style.styl -o style.css
You can also try all stylus features on stylus-lang.com, build something with stylus on codepen or integrate stylus with gulp using gulp-stylus or gulp-accord.
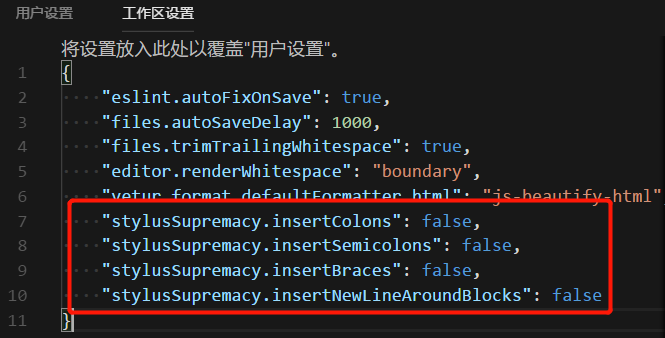
vscode中自动格式化stylus设置
安装 stylus Supremacy 插件
Stylus 特性
- 冒号可有可无
- 分号可有可无
- 逗号可有可无
- 括号可有可无
- 变量
- 插值(Interpolation)
- 混合(Mixin)
- 数学计算
- 强制类型转换
- 动态引入
- 条件表达式
- 迭代
- 嵌套选择器
- 父级引用
- Variable function calls
- 词法作用域
- 内置函数(超过 60 个)
- 语法内函数(In-language functions)
- 压缩可选
- 图像内联可选
- Stylus 可执行程序
- 健壮的错误报告
- 单行和多行注释
- CSS 字面量
- 字符转义
- TextMate 捆绑
选择器(Selectors)
缩排
Stylus 基于缩进,空格有重要的意义,使用缩排和凹排代替花括号{}
body
color white
对应于:
body {
color: #fff;
}
规则集
Stylus 就跟 CSS 一样,允许你使用逗号为多个选择器同时定义属性。
textarea, input
border 1px solid #eee
textarea
input
border 1px solid #eee
对应于:
textarea,
input {
border: 1px solid #eee;
}
父级引用&
字符&指向父选择器
textareainputcolor#A7A7A7&: hover color #000;
等同于:
textarea,
input {
color: #a7a7a7;
}
textarea:hover,
input:hover {
color: #000;
}
下面这个例子,IE 浏览器利用了父级引用以及混合书写来实现 2px 的边框。
box-shadow()
-webkit-box-shadow arguments
-moz-box-shadow arguments
box-shadow arguments
html.ie8 &,
html.ie7 &,
html.ie6 &
border 2px solid arguments[length(arguments) - 1]
body
#login
box-shadow 1px 1px 3px #eee
其变身后面目:
body #login {
-webkit-box-shadow: 1px 1px 3px #eee;
-moz-box-shadow: 1px 1px 3px #eee;
box-shadow: 1px 1px 3px #eee;
}
html.ie8 body #login,
html.ie7 body #login,
html.ie6 body #login {
border: 2px solid #eee;
}
unquote()
Stylus 无法处理的属性值,unquote()可以帮你
filter unquote('progid:DXImageTransform.Microsoft.BasicImage(rotation=1)')
生成为:
filter: progid:DXImageTransform.Microsoft.BasicImage(rotation=1);
变量(Variables)
变量
我们可以指定表达式为变量,然后在我们的样式中贯穿使用:
font-size = 14px
body
font font-size Arial, sans-seri
$font-size = 14px body {
font: $font-size sans-serif;
}
编译为:
body {
font: 14px Arial, sans-serif;
}
属性查找
Stylus 有另外一个很酷的独特功能,不需要分配值给变量就可以定义引用属性。属性会“向上冒泡”查找堆栈直到被发现,或者返回 null。
#logo
position: absolute
top: 50%
left: 50%
width: w = 150px
height: h = 80px
margin-left: -(w / 2)
margin-top: -(h / 2)
#logo
position: absolute
top: 50%
left: 50%
width: 150px
height: 80px
margin-left: -(@width / 2)
margin-top: -(@height / 2)
position()
position: arguments
z-index: 1 unless @z-index
#logo
z-index: 20
position: absolute
#logo2
position: absolute
插值(Interpolation){}
Stylus 支持通过使用{}字符包围表达式来插入值,其会变成标识符的一部分。例如,-webkit-{'border' + '-radius'}等同于-webkit-border-radius.
vendor(prop, args)
-webkit-{prop} args
-moz-{prop} args
{prop} args
border-radius()
vendor('border-radius', arguments)
button
border-radius 1px 2px / 3px 4px
变身:
button {
-webkit-border-radius: 1px 2px / 3px 4px;
-moz-border-radius: 1px 2px / 3px 4px;
border-radius: 1px 2px / 3px 4px;
}
选择器插值
table
for row in 1 2 3 4 5
tr:nth-child({row})
height: 10px * row
也就是:
table tr:nth-child(1) {
height: 10px;
}
table tr:nth-child(2) {
height: 20px;
}
table tr:nth-child(3) {
height: 30px;
}
table tr:nth-child(4) {
height: 40px;
}
table tr:nth-child(5) {
height: 50px;
}
运算符(Operators)
算符优先级
下表运算符优先级,从最高到最低:
[] //下标运算符`[]`允许我们通过索引获取表达式内部值
! ~ + -
is defined
/*
* 指数:**
* 2 ** 8 => 256
*
*/
** * / %
/*
* 加减:二元加乘运算其单位会转化,或使用默认字面量值。
* 5s - 1000ms => 4s
*
*/
+ -
/*
* 范围
* 1..5 => 1 2 3 4 5
* 1...5 => 1 2 3 4
*/
... ..
<= >= < >
/*
* 存在操作符:in 检查左边内容是否在右边的表达式中。
* 1 in 1 2 3 => true
*
*/
in
== is != is not isnt
is a //实例检查
&& and || or
?:
= := ?= += -= *= /= %=
not
if unless
铸造
作为替代简洁的内置unit()函数,语法(expr) unit可用来强制后缀。
body
n = 5
foo: (n)em
foo: (n)%
foo: (n + 5)%
格式化字符串
格式化字符串模样的字符串%可以用来生成字面量值,通过传参给内置s()方法。
'-webkit-gradient(%s, %s, %s)' % (linear (0 0) (0 100%))
// => -webkit-gradient(linear, 0 0, 0 100%)
混合书写(Mixins)
混入
混入和函数定义方法一致,但是应用却大相径庭。
例如,下面有定义的border-radius(n)方法,其却作为一个mixin(如,作为状态调用,而非表达式)调用。
当border-radius()选择器中调用时候,属性会被扩展并复制在选择器中。
border-radius(n)
-webkit-border-radius n
-moz-border-radius n
border-radius n
form input[type=button]
border-radius(5px)
编译成:
form input[type="button"] {
-webkit-border-radius: 5px;
-moz-border-radius: 5px;
border-radius: 5px;
}
使用混入书写,你可以完全忽略括号,提供梦幻般私有属性的支持。
border-radius(n)
-webkit-border-radius n
-moz-border-radius n
border-radius n
form input[type=button]
border-radius 5px
注意到我们混合书写中的border-radius当作了属性,而不是一个递归函数调用。
更进一步,我们可以利用arguments这个局部变量,传递可以包含多值的表达式。
border-radius()
-webkit-border-radius arguments
-moz-border-radius arguments
border-radius arguments
现在,我们可以像这样子传值:border-radius 1px 2px / 3px 4px!
另外一个很赞的应用是特定的私有前缀支持——例如 IE 浏览器的透明度:
support-for-ie?=trueopacity(n)opacitynifsupport-for-iefilterunquote('progid:DXImageTransform.Microsoft.Alpha(Opacity='+round(n * 100)+')')#logo
&: hover opacity 0.5;
渲染为:
#logo:hover {
opacity: 0.5;
filter: progid:DXImageTransform.Microsoft.Alpha(Opacity=50);
}
父级引用
混合书写可以利用父级引用字符&, 继承父业而不是自己筑巢。
stripe(even = #fff, odd = #eee)trbackground-colorodd&.even&: nth-child(even) background-color
even;
然后,利用混合书写,如下:
table
stripe()
td
padding 4px 10px
table#users
stripe(#303030, #494848)
td
color white
方法(Functions)
函数
Stylus 强大之处就在于其内置的语言函数定义。其定义与混入(mixins)一致;却可以返回值。
返回值
很简单的例子,两数值相加的方法:
add(a, b)
a + b
我们可以在特定条件下使用该方法,如在属性值中:
body
padding add(10px, 5)
渲染:
body {
padding: 15px;
}
默认参数
可选参数往往有个默认的给定表达。在 Stylus 中,我们甚至可以超越默认参数。
add(a, b = a)
a + b
add(10, 5)
// => 15
add(10)
// => 20
多个返回值
Stylus 的函数可以返回多个值,就像你给变量赋多个值一样。
sizes = 15px 10px
sizes[0]
// => 15px
条件
比方说,我们想要创建一个名为stringish()的函数,用来决定参数是否是字符串。我们检查val是否是字符串或缩进(类似字符)。
stringish(val)
if val is a 'string' or val is a 'ident'
yes
else
no
变量函数
我们可以把函数当作变量传递到新的函数中。例如,invoke()接受函数作为参数,因此,我们可以传递add()以及sub().
invoke(a, b, fn)
fn(a, b)
add(a, b)
a + b
body
padding invoke(5, 10, add)
padding invoke(5, 10, sub)
参数
arguments是所有函数体都有的局部变量,包含传递的所有参数。
sum()
n = 0
for num in arguments
n = n + num
sum(1,2,3,4,5)
// => 15
内置方法(Built-in Functions)
red(color) 返回 color 中的红色比重。
green(color) 返回 color 中的绿色比重。
blue(color) 返回 color 中的蓝色比重。
alpha(color) 返回 color 中的透明度比重。
dark(color) 检查 color 是否是暗色。
light(color) 检查 color 是否是亮色。
hue(color) 返回给定 color 的色调。
saturation(color) 返回给定 color 的饱和度。
lightness(color) 返回给定 color 的亮度。
push(expr, args…) 后面推送给定的 args 给 expr.
nums = 1 2
push(nums, 3, 4, 5)
nums
// => 1 2 3 4 5
unshift(expr, args…) 起始位置插入给定的 args 给 expr.
nums = 4 5
unshift(nums, 3, 2, 1)
nums
// => 1 2 3 4 5
keys(pairs) 返回给定 pairs 中的键。
values(pairs) 返回给定 pairs 中的值。
typeof(node) 字符串形式返回 node 类型。
type(12)
// => 'unit'
typeof(#fff)
// => 'rgba'
unit(unit[, type]) 返回 unit 类型的字符串或空字符串,或者赋予 type 值而无需单位转换。
unit(10)
// => ''
unit(15in)
// => 'in'
unit(15%, 'px')
// => 15px
unit(15%, px)
// => 15px
match(pattern, string) 检测string是否匹配给定的pattern.
abs(unit)绝对值。
ceil(unit) 向上取整。
floor(unit) 向下取整。
round(unit)四舍五入取整。
min(a, b)取较小值。
max(a, b)取较大值。
even(unit)是否为偶数。
add(unit)是否为奇数。
sum(nums)求和。
avg(nums)求平均数。
join(delim, vals…)给定 vals 使用 delim 连接。
join(' ', 1 2 3)
// => "1 2 3"
join(',', 1 2 3)
// => "1,2,3"
s(fmt, …)
s()方法类似于unquote(),不过后者返回的是 Literal 节点,而这里起接受一个格式化的字符串,非常像 C 语言的 sprintf(). 目前,唯一标识符是%s.
s('bar()');
// => bar()
s('bar(%s)', 'baz');
// => bar("baz")
s('bar(%s)', baz);
// => bar(baz)
s('bar(%s)', 15px);
// => bar(15px)
s('rgba(%s, %s, %s, 0.5)', 255, 100, 50);
// => rgba(255, 100, 50, 0.5)
s('bar(%Z)', 15px);
// => bar(%Z)
s('bar(%s, %s)', 15px);
// => bar(15px, null)
为表现一致检测这个%字符串操作符。
length([expr]) 括号表达式扮演元组,length()方法返回该表达式的长度。
warn(msg) 使用给定的 error 警告,并不退出。
error(msg) 伴随着给定的错误 msg 退出。
last(expr)返回给定 expr 的最后一个值。
p(expr)检查给定的 expr.
opposite-position(positions)返回给定 positions 相反内容。
image-size(path)
返回指定path图片的width和height. 向上查找路径的方法和@import一样,paths设置的时候改变。
width(img);
return image - size(img)[0];
height(img);
return image - size(img)[1];
image - size("tux.png");
// => 405px 250px
image - size("tux.png")[0] == width("tux.png");
// => true
注释(Comments)
Stylus 支持三种注释,单行注释,多行注释,以及多行缓冲注释。
单行注释
跟 JavaScript 一样,双斜杠,CSS 中不输出。
// 我是注释!
body
padding 5px // 蛋疼的padding
多行注释
多行注释看起来有点像 CSS 的常规注释。然而,它们只有在 compress 选项未启用的时候才会被输出。
/*
* 给定数值合体
*/
add(a, b)
a + b
多行缓冲注释
跟多行注释类似,不同之处在于开始的时候,这里是/*!. 这个相当于告诉 Stylus 压缩的时候这段无视直接输出。
/*!
* 给定数值合体
*/
add(a, b)
a + b
条件(Conditionals)
条件
if / else if / else
overload-padding = true
if overload-padding
padding(y, x)
margin y x
body
padding 5px 10px
除非(unless)
熟悉 Ruby 程序语言的用户应该都知道unless条件,其基本上与 if 相反,本质上是(!(expr)).
下面这个例子中,如果disable-padding-override是undefined或false, padding 将被干掉,显示 margin 代替之。但是,如果是 true, padding 将会如期继续输出 padding 5px 10px.
disable-padding-override = true
unless disable-padding-override is defined and disable-padding-override
padding(x, y)
margin y x
body
padding 5px 10px
后缀条件
Stylus 支持后缀条件,这就意味着 if 和 unless 可以当作操作符;当右边表达式为真的时候执行左边的操作对象。
pad(types = margin padding, n = 5px)
padding unit(n, px) if padding in types
margin unit(n, px) if margin in types
body
pad()
body
pad(margin)
body
apply-mixins = true
pad(padding, 10) if apply-mixins
生成为:
body {
padding: 5px;
margin: 5px;
}
body {
margin: 5px;
}
body {
padding: 10px;
}
迭代(Iteration)
迭代
Stylus 允许你通过for/in对表达式进行迭代形式如下:
for <val-name> [, <key-name>] in <expression>
如何使用<key-name>:
body
fonts = Impact Arial sans-serif
for font, i in fonts
foo i font
生成为:
body {
foo: 0 Impact;
foo: 1 Arial;
foo: 2 sans-serif;
}
关键字
@import
@media
@font-face
@keyframes
@extend
内联Data URI图像
Stylus 捆绑了一个可选函数,名叫 url(),其替换了字面上的 url()调用(且使用 base64 Data URIs 有条件地内联它们)。
示例
通过 require('stylus').url 该函数本身是可用的,其接受一个 options 对象,当看到 url()时候,返回 Stylus 内部调用的函数。
.define(name, callback)方法指定了一个可被调用的 JavaScript 函数。在这种情况下,因为我们图片在./css/images 中,我们可以忽视 paths 选项(默认情况下,会查找相关要呈现的图像文件)。如果愿意,该行为时可以改变的。
stylus(str)
.set("filename", __dirname + "/css/test.styl")
.define("url", stylus.url())
.render(function(err, css) {});
字符转码(Char Escaping)
转码
Stylus 可以字符转码。这可以让字符变成标识符,或是渲染成字面量。
例如:
body
padding 1 \+ 2
编译成:
body {
padding: 1 + 2;
}
注意 Stylus 中/当作为属性使用的时候需要用括号括起来:
body
font 14px/1.4
font (14px/1.4)
生成:
body {
font: 14px/1.4;
font: 10px;
}